RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
The respiratory system’s primary function is to breathe in air, absorb oxygen into the bloodstream, and breathe out carbon dioxide.
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM STEPS
First step
Sixth step
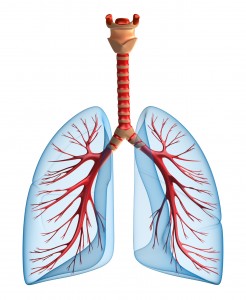
MAIN PARTS OF YOUR RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Lungs
Are a pair of spongy, air-filled organs located on either side of the chest (thorax).
This is your main windpipe, which starts at the back of your throat.
-
- Epiglottis
Alveoli
These are the tiny air sacs that connect to each bronchiole. Blood passes through here, exchanging fresh oxygen from the air for carbon dioxide to be carried back out and exhaled.
HOW THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM WORKS
Oxygen enters the nose or mouth.The air then passes through the sinuses which help to regulate the temperature and humidity.
As air goes through the trachea, it is filtered more and enters the bronchi.
The bronchi are lined with tiny hairs called cilia which move back and forth and carry mucus up and out. (Note: Mucus, a sticky fluid, collects dust and that have invaded the lungs. We get rid of it when we sneeze, cough, spit or swallow.)
The bronchial tubes lead to the lobes of the lungs. (The right lung has three lobes; the left lung has two.) Lobes are filled with small, spongy sacs called alveoli. This is where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs.
The alveolar walls are extremely thin and are composed of a single layer of tissues called epithelial cells and tiny blood vessels (pulmonary capillaries).
Blood passes through the capillaries. The pulmonary artery carries blood containing carbon dioxide to the air sacs, where the gas moves from the blood to the air. Oxygenated blood goes to the heart through the pulmonary vein, and the heart pumps it throughout the body.

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario